Sustainable Construction & Resources

How might building technology, construction innovation, or automation be utilized to scale?
What alternatives exist for conventional stick-frame construction and housing models?
Are proposals for “missing middle housing” meeting the demand of contemporary families and their communities?
Can Michigan and other locations within the Great Lakes region become hubs for the manufacturing of timber building components?
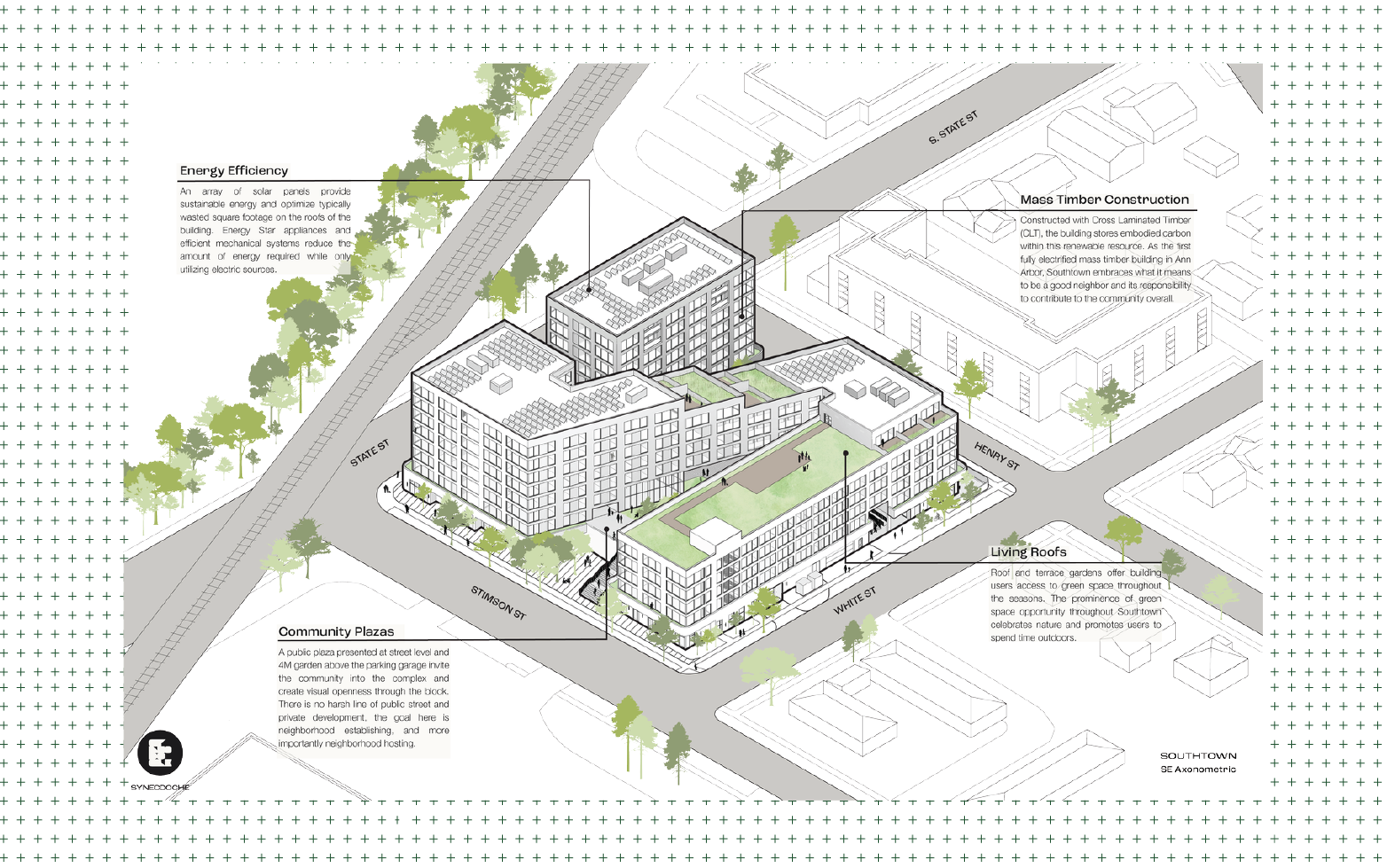
Design: SouthTown by 4M
Synecdoche, Lisa Sauve and Adam Smith
SouthTown is a proposed mixed-use fully electrified building built with mass timber construction in downtown Ann Arbor.
The project provides on-site solar energy, bike parking, vehicle parking, outdoor community spaces, pedestrian connections, and a variety of living spaces, increasing the Ann Arbor housing supply overall. Using WELL v2 standards to inform the design, the project will create healthy living and working environments for people.
The embodied carbon within the structural application and systems designed to rely on an infrastructure to deliver only renewable energy show the understanding of responsible techniques that can create energy, housing, and resources to a broader connection.
Design: The Canopy
PLY+, Craig Borum and Jen Maigret
Following on the heels of a previous single-family residential development scheme that proposed to clear-cut the site and was shut down by neighborhood outcry, The Canopy consolidates the same residential density into a 5-story bar, slightly curved to minimize the visual impact on adjacent neighbors and oriented to maximize the harvest of solar energy on-site.
A range of unit sizes and configurations provide a mix of affordability benchmarks. Balconies to the south extend the living spaces outdoors to nestle beneath the 75′ – 85′ canopy of landmark
walnuts, hickory and bur oaks. The north side is unified by a lightweight trellis as a façade to facilitate the “greening” of its entry with vines grown from the north, east and west grounds of the site.
Novel configurations of heating and cooling technologies including heat pumps, solar thermal recovery and graywater thermal recovery minimize operational energy loads and the solar PV canopy balances this demand through its annual production. In sum, the project provides a new model of housing density in a neighborhood seeking to preserve the heritage landscape.